Background:
The current monsoon spell that started in the second week of July 2022 has caused widespread flooding and has led to extensive human and infrastructure damage across many parts of Pakistan. The Government of Pakistan estimates that around 33 million people across the country are affected by the rains, floods and consequent impacts such as landslides. More than 421,000 refugees living in calamity-declared districts are also affected or at risk. As of August 2022, some 6.4 million people are estimated to need of assistance.[1]
According to the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)’ Monsoon Situation Report on August 30, 2022, around 1,057,388 houses were damaged (including 324,386 fully and 733,002 partially damaged). In addition to this, around 5063 KM roads have been washed away, 243 bridges have collapsed, and 730,483 animals have died.
Southern and central Pakistan have been most affected, particularly Balochistan and Sindh provinces. Balochistan has received 5.1 times its 30-year average rainfall as of 27 August, while Sindh’s is 5.7 times its 30-year average. b
Death and injury is extensive and likely higher because of unreported number in Balochistan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP), and Sindh provinces. In the same vein, livestock and agriculture was impacted threatening food security. In addition, the floods are expected to strain existing healthcare services as gastrointestinal illnesses, malaria, skin infections, snake bites and injuries are anticipated to increase significantly.
Current situation and implications for Pakistan, Sindh province
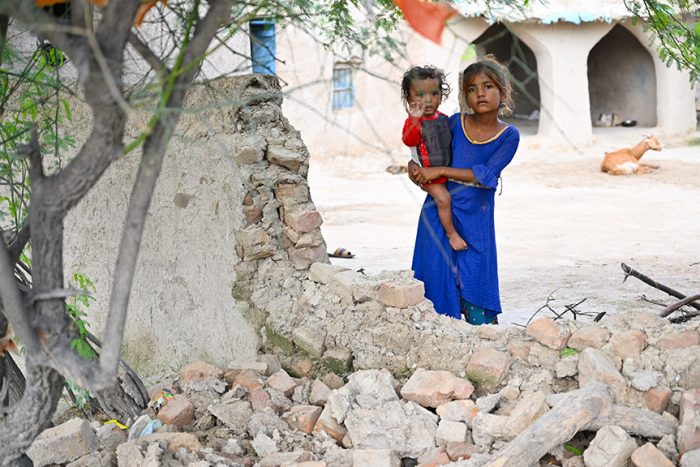
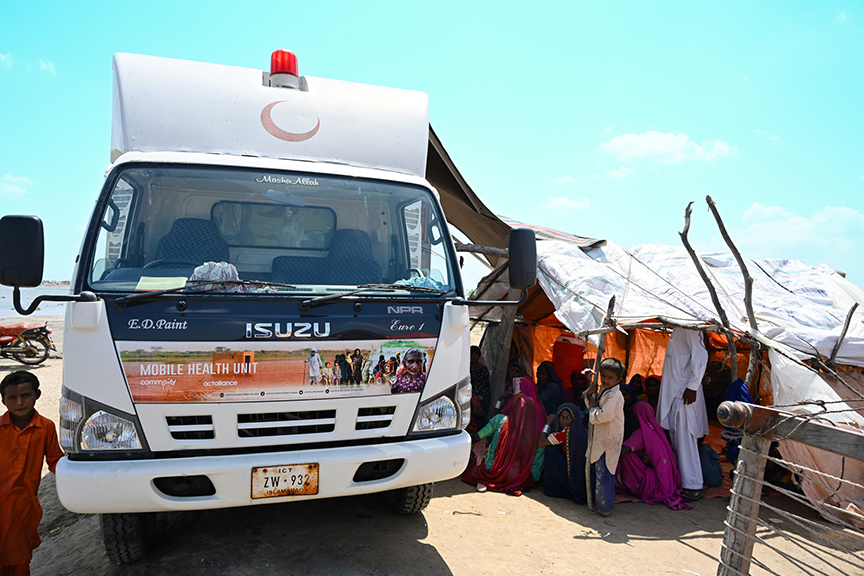
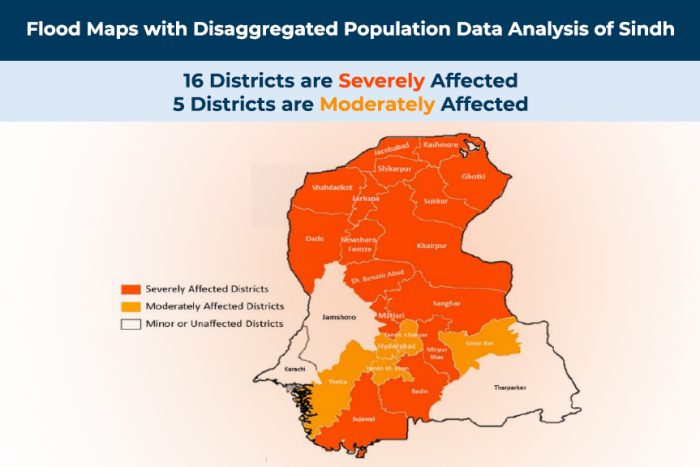
Sindh province is affected most adversely by heavy rainfall and resultant flooding in Pakistan. Over 110 districts have declared a state of emergency in Sindh province. According to the Provincial Disaster Management Authority of Sindh, over 240,000 people remain displaced in the province as of 3 December 2022. Nearly 90% of flood-displaced people are reportedly with host communities, while the remaining are in tent cities and relief camps. While receding flood waters have allowed millions of people to go home, there are reports of significant service gaps in areas of return, in addition to extensive impacts to homes, agriculture, and livelihoods. In general, access to clean food, water, clothing, shelter and the ability to find safe areas to rest and sleep has and continues to be a challenge.
Public health concerns are high due to damaged infrastructure, stagnating water and inadequate sanitation facilities. In Sindh, between July and early October, nearly 350,000 people were suspected of having malaria, more than 700,000 had some form of diarrhea, and over 770,000 people reported skin-related diseases. The practice of open defecation has increased from one-fifth before the floods to over one-third of the affected population, with 6 million no longer having home sanitation facilities.[2]
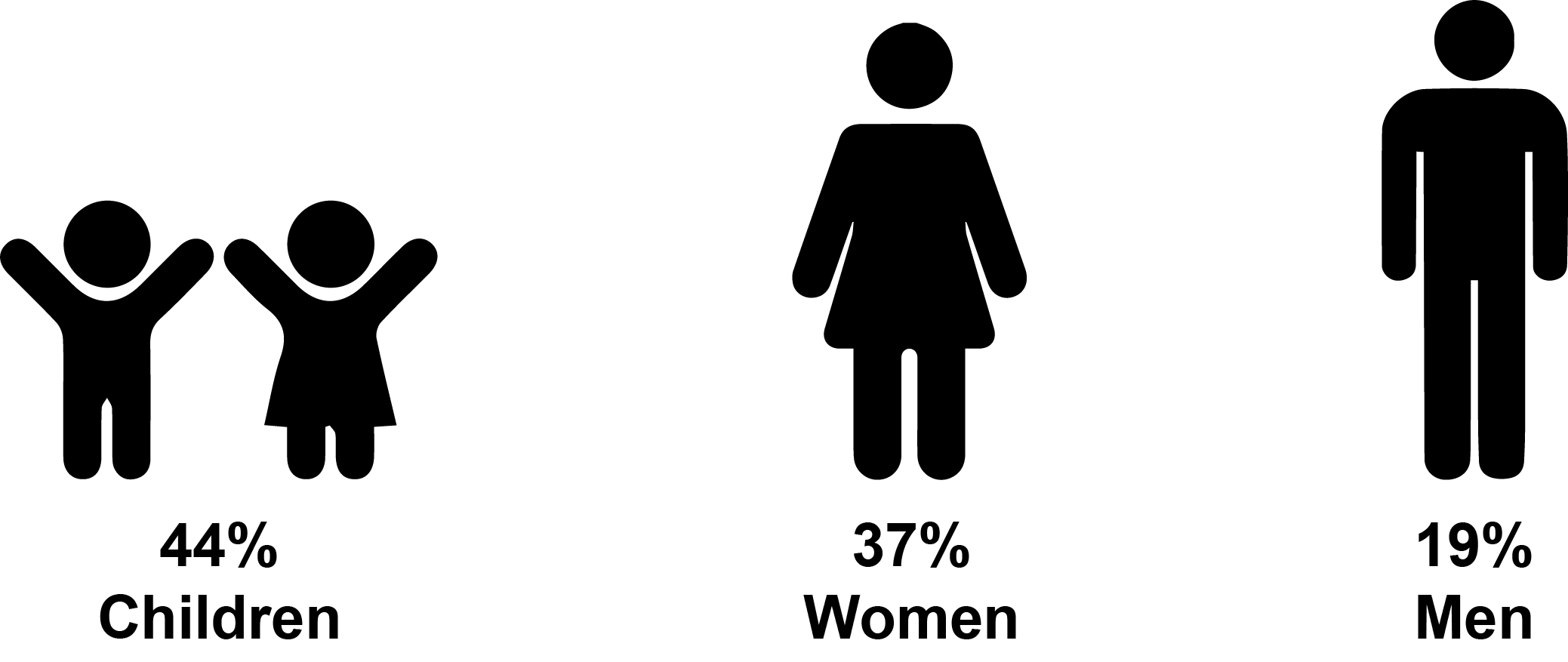
Women and girls are vulnerable to sexual exploitation and abuse because safeguarding measures are not designed into the programmes by the organisations. Protective mechanisms such as safe spaces and support services have either been destroyed or no longer exist. Moreover, women play a large role in the household, as such, access to clean water for cooking, cleaning and toileting no longer exist. Similarly, the services such as information provision, participation, and feedback are unavailable to them and other vulnerable groups resulting in being excluded from the participatory approach at all levels.
Overview of Damage in Sindh (according to Provincial Disaster Management Authority (PDMA) Sindh from June to Dec 2022)[3]:
- 8,422 people injured
- 801 deaths
- 436,435 Livestock Perished
- 642,672 houses partially Damaged, 1,415,677 houses fully damaged
- 3,777,272 acres of land damaged
- 12,356,860 people affected
- 194,562 people displaced
- 59 health facilities fully damaged and 461 partially damaged[4]
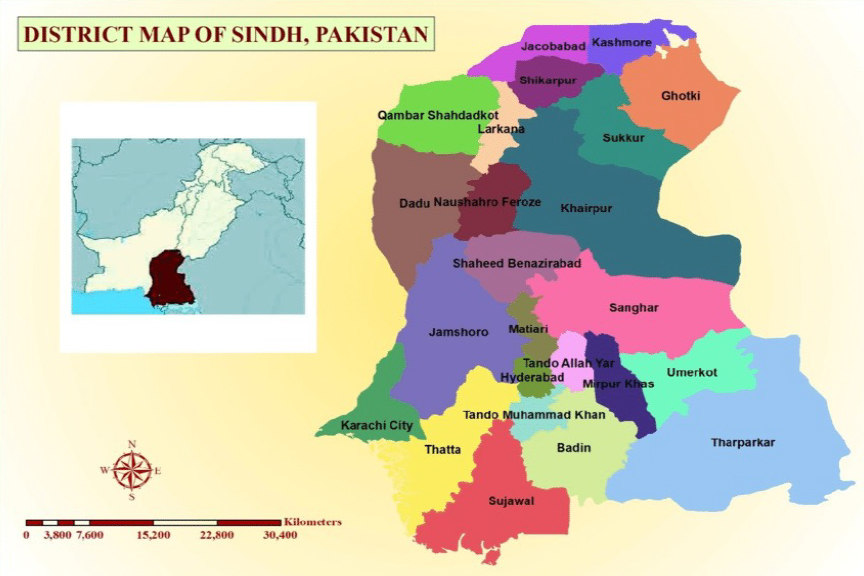
Geographical focus of CWSA: Sindh, Pakistan
Recommended programming for recovery and rehabilitation in the following areas:
- Food/cash assistance – to reduce food consumption gaps and supporting populations as they restore livelihood and/or livestock.
- Reconstruction/rehabilitation of livestock and agriculture – replacement of lost livestock, rehabilitating surviving livestock, restoration of agricultural produce, reconstruction of animal shelters, re-establishing irrigation infrastructure and equipment as part of restoring livelihoods amongst impacted populations.
- Cash assistance/cash for food/cash for work – These efforts are targeted towards disaster risk reduction (DRR) in that strategies are implemented to prevent new disaster risks, reducing existing disaster and managing residual risks in order to strengthen resilience and reduction of disaster related losses.
- Shelter – with the view of mitigating gender-based violence, exploitation of children etc. as a consequence of displacement. Moreover, the provision and utilization of shelter packs that are procured using local materials to flood-proof homes as part of overall DRR strategies.
- Healthcare services – provision of essential medicines, menstrual hygiene products, and malarial treatment in an effort to support existing medical services. In addition, leveraging existing public health clinics and local government facilities that are in need of rehabilitation and improvement. Integrated Sexual Reproductive Health (SRH), clean delivery kits/newborn baby kits, capacity building of local health workers (LHWs, Marvi workers).
- Quality & accountability (Q&A) – To mainstream Q&A across humanitarian organizations and Accountability Learning Working Group (ALWG) organizations, systems, tools, procedures and standards and to undertake capacity building in Q&A and Safeguarding of staff. Also, to develop resources in local languages for dissemination on a wider scale.
- Education – De-watering, cleaning, and disinfection of schools to facilitate the resumption of educational activities in a safe and healthy learning environment, distribution of educational teaching and learning materials, training teachers on psychosocial support, multi-grade teaching and teaching in emergencies, training and mobilization of School Management Committee (SMC) members on psychosocial support, safe school reopening, and functioning of schools. Programs to build teacher’s capacity on the learning environment, teachers’ trainings on positive learning environment (PLE), teachers training on early childhood care and education (ECCE) and play based learning activities.
[1] https://reliefweb.int/report/pakistan/pakistan-2022-floods-response-plan-01-sep-2022-28-feb-2023-issued-30-aug-2022
[2] https://reliefweb.int/report/philippines/asia-and-pacific-weekly-regional-humanitarian-snapshot-25-31-october-2022
[3] https://reliefweb.int/report/pakistan/provincial-disaster-management-authority-pdma-sindh-daily-situation-report-december-14-2022
[4] https://reliefweb.int/report/philippines/asia-and-pacific-weekly-regional-humanitarian-snapshot-25-31-october-2022