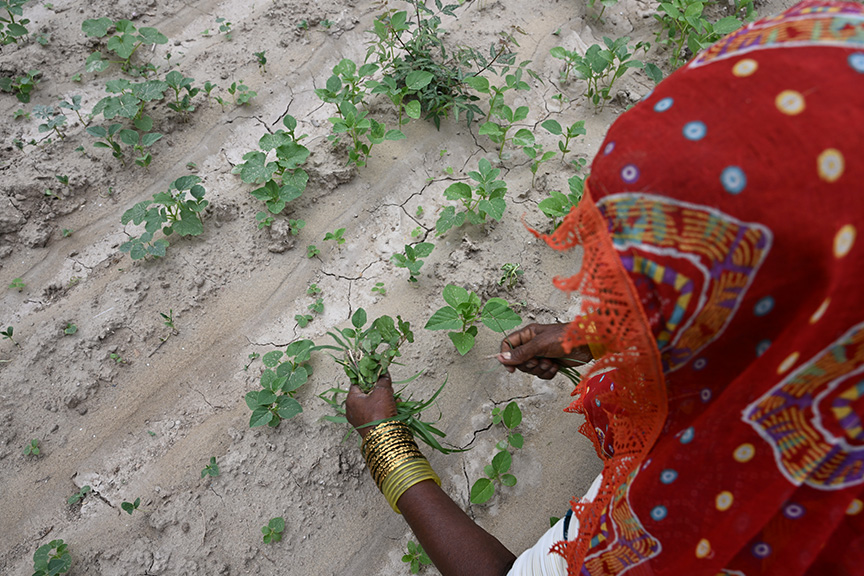
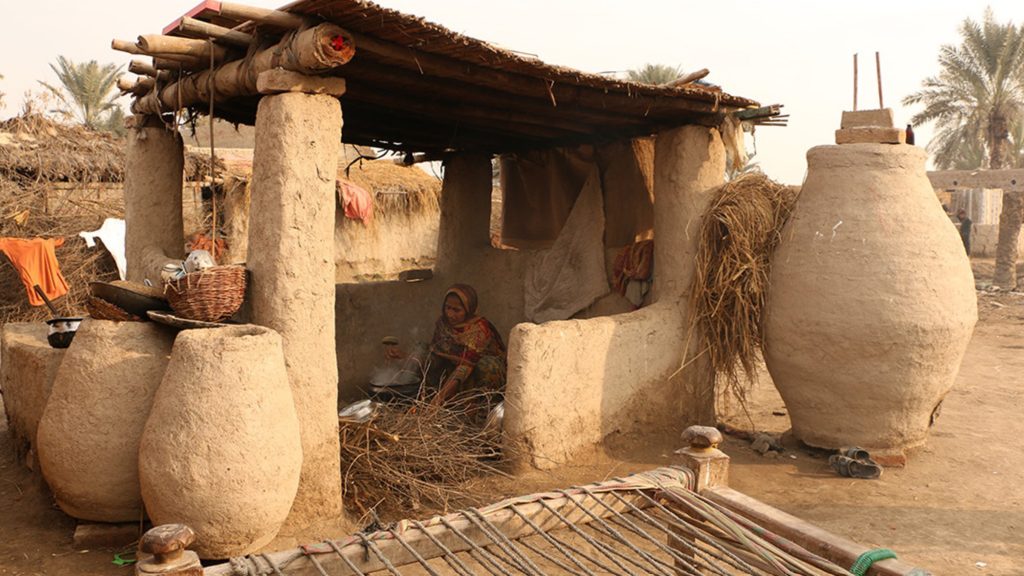
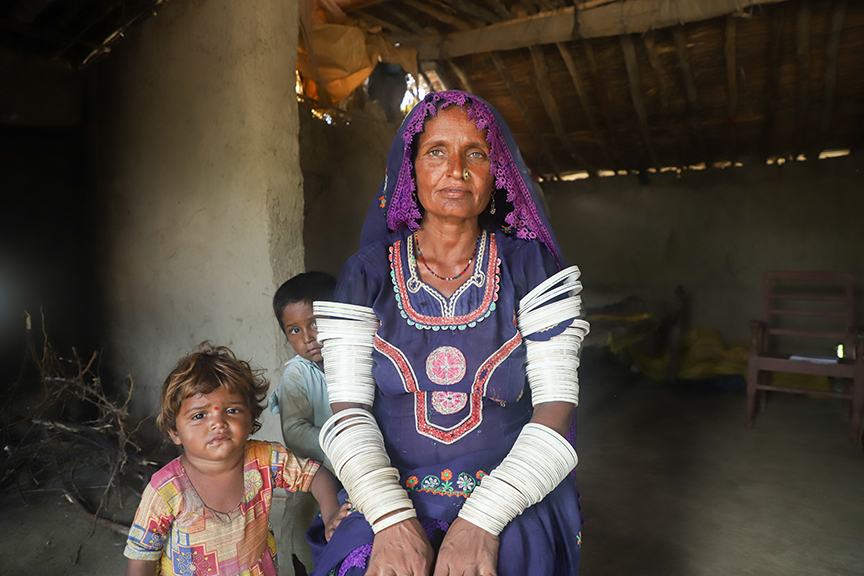
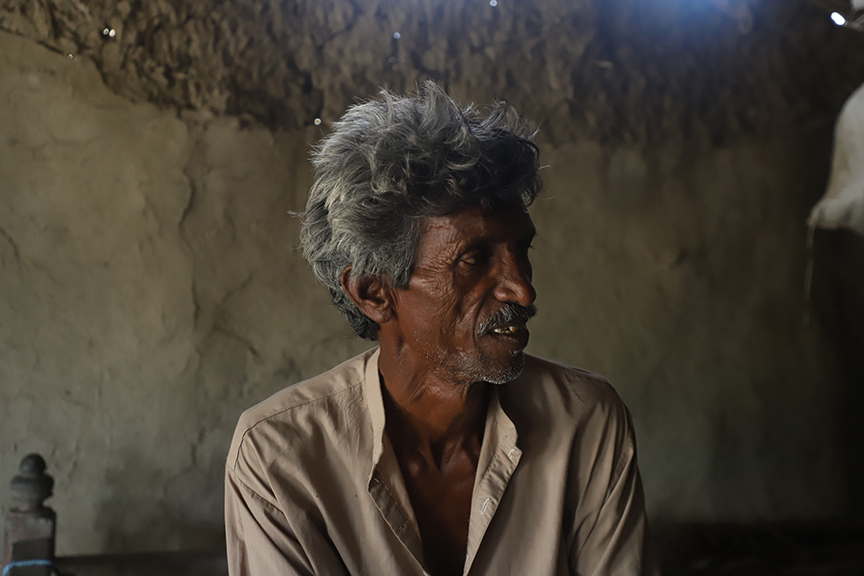
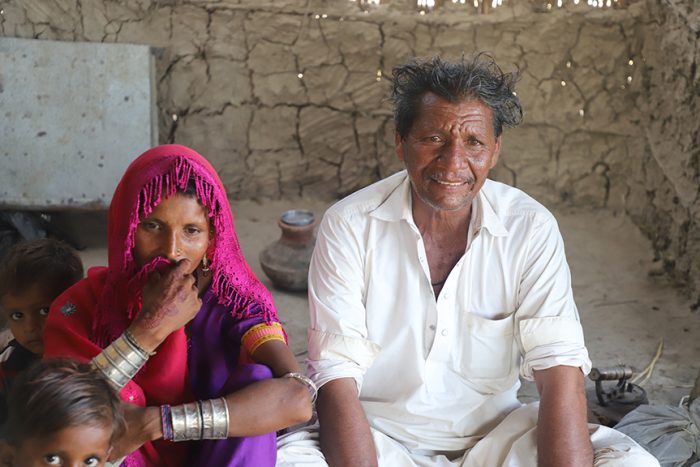
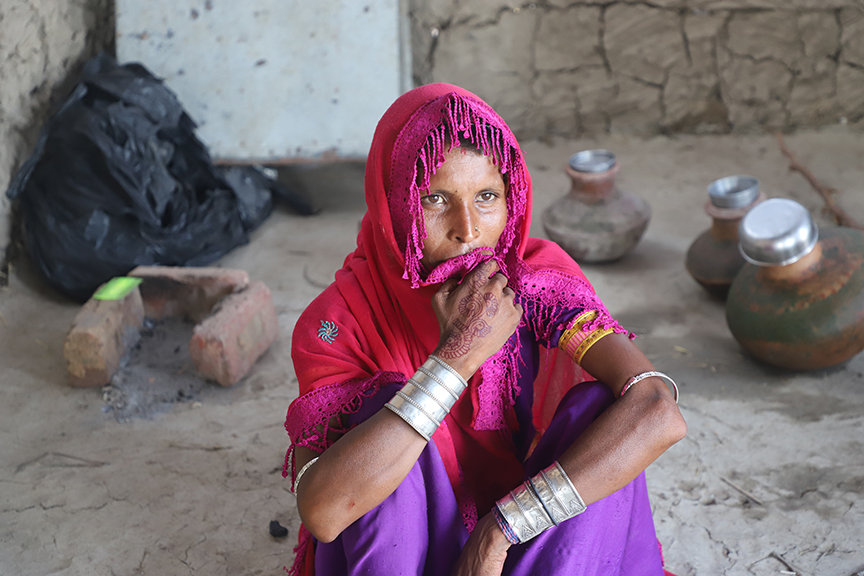
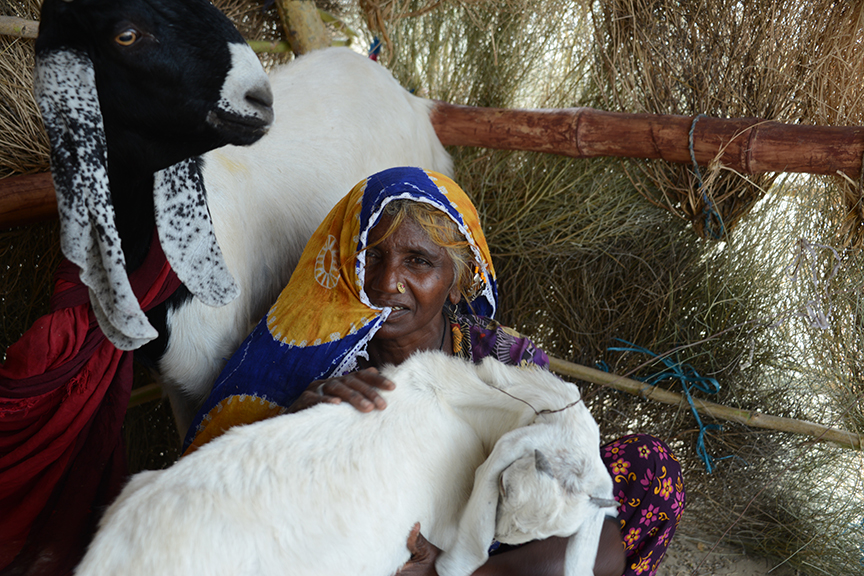
Lal Ji, his wife and three children of village Umeed Ali Chandio just outside Nabisar (Umerkot district) live in a very neat, well-kept, almost picturesque home. He is a landless farmer who works eight acres of a landlord’s holding and shares the proceeds with the owner. But he blindly followed farming procedures unchanged for centuries. He cites the example of how millets, guar and mauth lentils were sowed all together in the same plots despite each having a different ripening time.
“When the first crop was ready and we harvested, we damaged nearly half of the remaining unripe species underfoot and with the sickle. That was the way passed down to us by our elders and it simply did not occur to us that planting each specie in separate plots could double the yield of those ripening later. It had to be the staff and trainers of this organisation (Community World Service Asia (CWSA)) to teach us how to do the right thing under!” says Lal Ji.
Asked why it was like that and why he or other farmers did not think logically to increase their yield, Lal Ji simply shrugs and says that was the way of the elders. “But now we are awakened and I am myself surprised how such a simple thing eluded us,” he adds.
If that ancient practice put Thar farmers at a disadvantage, the periodic disasters added to the deterrent. In 2021, Thar was invaded by a pestilence of locust. That year Lal Ji had invested PKR 40,000 (Approx. USD 143) in the eight acres he was farming. This sum had all been borrowed from the landlord and when the locusts wiped out every last bit of green from his fields. He went under debt and had to live by selling off some of his livestock. The year that followed was hardly any better. If there was no locust, the summer rains failed and once again Lal Ji kept body and soul together by disposing off some more of his livestock.
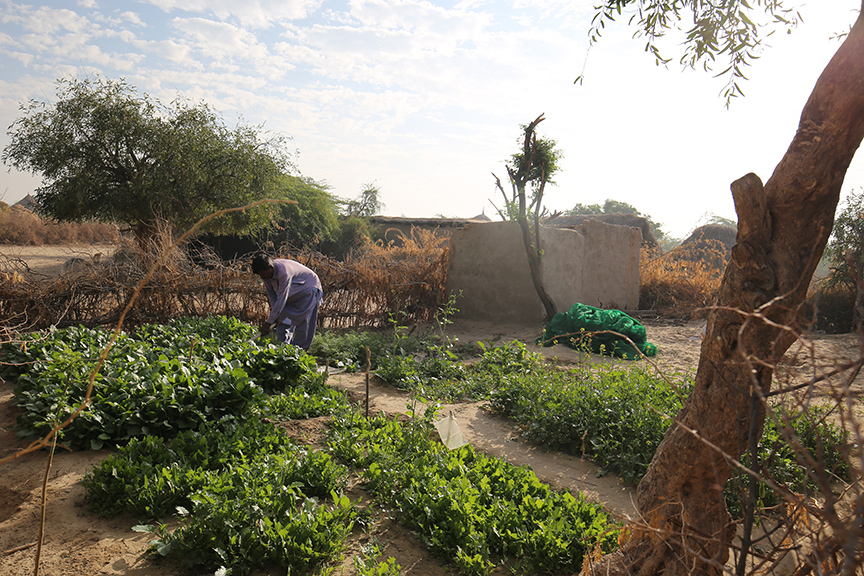

The beginning of 2022 brought in succour. The multi-purpose cash grant, agricultural and vegetable seeds together with training under CWSA & DKH’s food security and livelihood support, smoothed the bumpy road Lal Ji was treading. His excitement about learning to plant millets, guar and mauth in different plots is still viable two years after learning this evident truth. The cash grant helped him pay off his debt and the year when the rest of Sindh was drowned out by the worst deluge known in living memory, his fields in the troughs of the dunes did well with the natural irrigation.
In December 2023, he recounted how he had harvested 400 kilograms each of millets, guar beans and mauth. The millets he kept for his family while the rest he sold. However, being the judicious man that he is, Lal Ji retained enough seeds for his 2024 summer plantation.
Another thing that Lal Ji and the others learned in the training was that selling the harvest wholesale fetched better prices. Earlier they would be approached by the bania (Indian caste consisting generally of moneylenders or merchants) from town who would offer the farmers a price for the standing crop. Since these poor farmers did not have the means to truck their harvest to the market, they reluctantly accepted the offer even when they knew it was fifty percent below the market price. Those who did not, would harvest and pack 40-kilogram sacks to haul to market by donkey as and when they required cash. Though they got marginally more per kilogram than selling the standing crop, the price was still below the market rate.
The training taught them to work cooperatively. In late 2022, when the separately planted crops were nearing harvest, the bania arrived with his offer only to be disappointed. He was told that this time the farmers were to bring their goods to him. And so, Lal Ji and five others filled up their sacks, hired a pick-up truck and hauled the harvest to the market where they sought the best buyer. The profit astonished the group. Once again Lal Ji is amazed why they had not thought of this simple mechanism by themselves.
It takes motivation, a bit of awareness raising and the freedom from worry for communities to think of the future. Following the first CWSA intervention, the village organisation repeatedly beset the District Education Officer and got a regular teacher for the village school who, they insisted, must be a local person and not from another district. This was to ensure interest and regular presence. The teacher, a Nabisar young man, now attends school daily.

Meanwhile, Lal Ji sends his two sons and daughter to the school in Nabisar town. They walk the three kilometres to and fro. For pre-teenage children that’s a tough walk through the sand, but Lal Ji says that the produce of the kitchen garden has added so much vigour to their lives for the children to even be tired when they return in the afternoon. “They also take PKR 20 each for something to eat from their school tuck shop,” says the man.
Sixty rupees daily sounds expensive and Lal Ji says he had always given his children this daily allowance. In days of adversity, he borrowed the sum from the village shop keeper. Now he gives it out from his own purse.
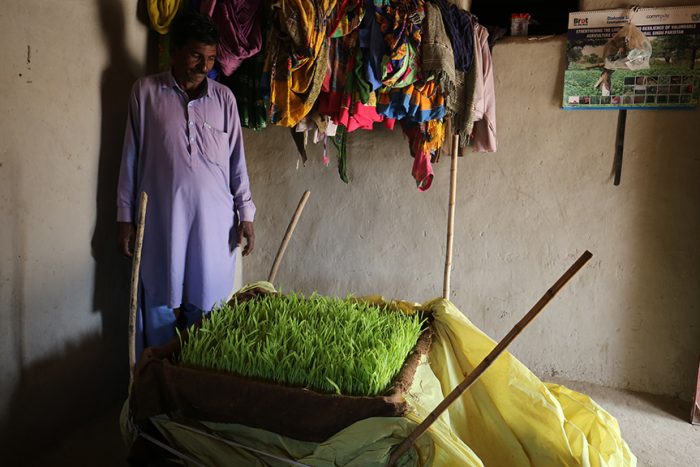
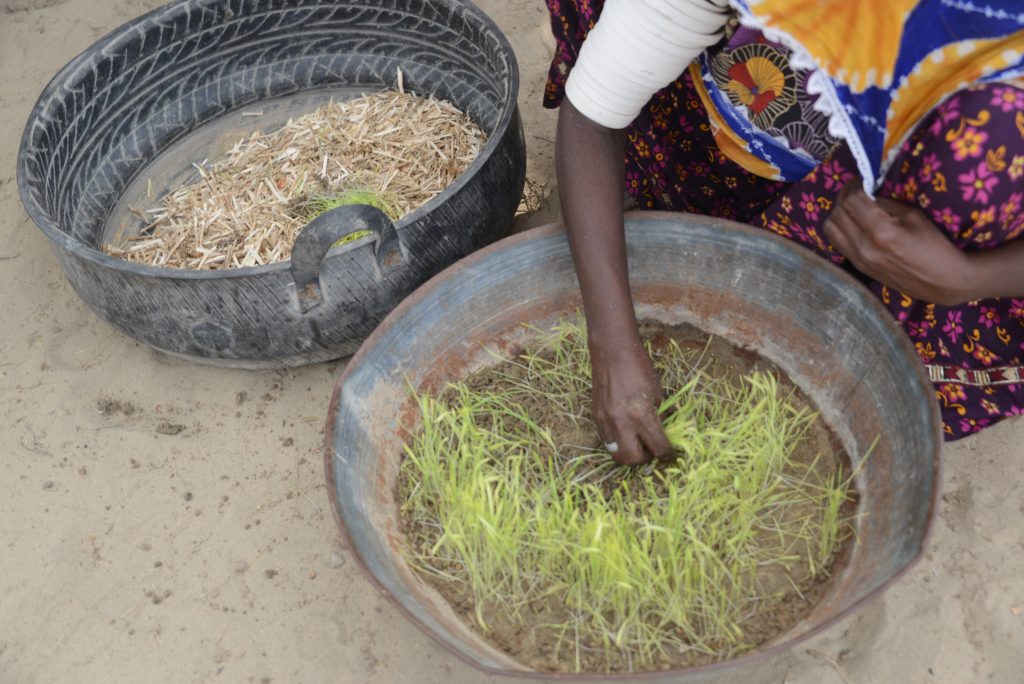
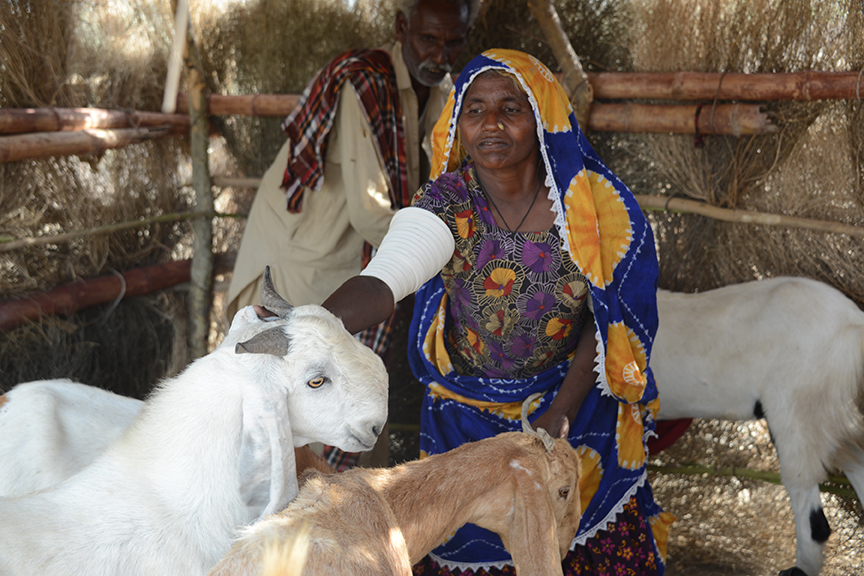
Almost breathless in his narration Lal Ji moves on to the boon of hydroponic agriculture. It is the greatest discovery in Lal Ji’s vocabulary. He shows off his trays of young maize seedlings and narrates how he has already fed one round of this miracle to his three goats even as the second is ready for cutting. The two goats that are in milk have markedly increased yield and his wife is able to give the three children half a glass each with breakfast.
A few houses away, young Bilawal is a livestock keeper with thirty goats who had long supplied the village with dairy products. He too has hydroponic trays in a shed for his livestock and has already fed his livestock three rounds from them. He says his four trays are too few for his stock and plans to increase them to twelve.
“Earlier I got not more than 250 ml of milk a day from each goat. This hydroponic feed is always available, even in the driest part of summer. And now my goats yield twice as much milk,” recounts Bilawal. From the five to six litres of milk from ten lactating goats he produces yogurt and clarified butter (ghee). While the yogurt is used at home, the ghee is a cash produce.
Bilawal says that livestock feed was always a problem during the drier months of summer. As a result, milk output almost dried up during those times. But since he has discovered hydroponic gardening, his goats are yielding very well. If things go well, Bilawal hopes to add a couple of buffaloes to his stock before the end of 2024.
It seems the livestock farmers of village Umeed Ali Chandio have hit the lode.