When: 2nd December, 2020
What time: 1:00PM to 2:30PM (Pakistan Standard Time)
Where: ZOOM – Link to be shared with registered participants – Register Here
Language: English
How long: 90 minutes
Who is it for: Humanitarian and development professionals, academics and UN staff committed to Quality and Accountability standards and approaches for principled actions
Format: Presentations, Discussion, Experience Sharing
Moderator & Presenter: Ester Dross
Background
The 2020 Regional NGO Partnership Events are a series of consultations and webinars, that will bring key humanitarian actors — local and national NGOs, INGOs, NGO networks, Red Cross and Crescent Movement, UN agencies, academics and others together for focused discussions and perspective sharing on how disaster risk reduction, emergency preparedness and humanitarian response should transform in this changing context. These events are organised collaboratively by the Asian Disaster Reduction and Response Network (ADRRN), International Council of Voluntary Agencies (ICVA), UN Office for Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA), and Community World Service Asia.
The 2020 Regional NGO Partnership Events will be an online learning and exchange journey of three months, starting with a consultative meeting on ‘the future of humanitarian response in Asia and the Pacific’, followed by various consultations and webinars, and a research that will produce a policy paper on the sector’s future in the region.
ADRRN’s Quality and Accountability (Q&A) thematic hub is hosted by Community World Service Asia. The focus of the hub is to strengthen principled humanitarian action in the region through promoting Q&A standards, approaches and principles among ADRRN members. The Q&A hub is organising webinars and panel discussions around different themes on Q&A during the 2020 Regional Partnership Events which will result in a position paper that will advocate for continuous mainstreaming of Q&A.
About the Event:
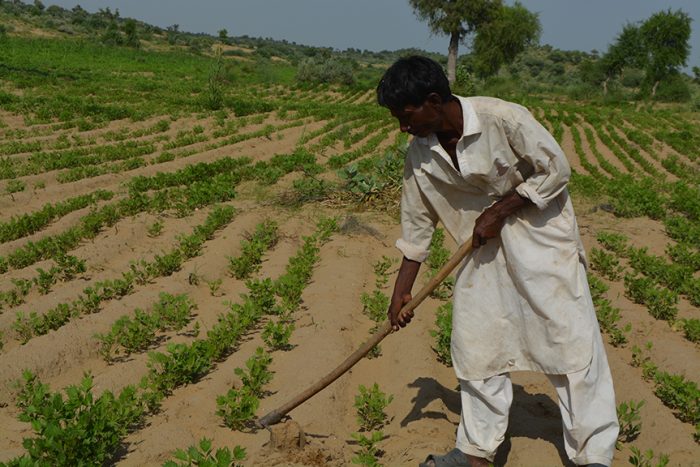
Complaints handling is a key component to any safeguarding framework and remains one of the great challenges in organisational efforts to improve accountability, close the gap and listen to people’s voices. To be compliant to this commitment, we need not only to prevent sexual exploitation and abuse, but act upon received reports. For this to happen, we need to proactively facilitate reception of such complaints.
This webinar will build upon the webinar organised earlier in May this year where basic issues such as key components of establishing CRM, while taking into account increased challenges of the Covid-19 crisis were discussed. Recent public reports demonstrate once again that, even when such systems are established, reporting remains low. The How to Make Complaint Response Mechanism Participatory & Responsive webinar in December therefore seeks to explore the reasons for the lack of reports, how to establish trust within communities through improved communication and identifying ways of ensuring better dialogue.
 Ester Dross—Independent Consultant
Ester Dross—Independent Consultant
Ms. Dross is an independent consultant with over 25 years of experience, specializing in accountability, prevention of sexual exploitation and abuse, gender and child protection.
Ms. Dross has had an extensive exposure to humanitarian certification systems and accountability to affected populations while working with HAP International as their Complaints Handling and Investigation Advisor, later as their Certification Manager. She has been closely involved in the Building Safer Organizations Project since 2005, dealing with sexual exploitation and abuse of beneficiaries, particularly focusing on gender and child protection. Over the last 6 years and since working as an independent consultant, Ester has been leading a pilot project for FAO on accountability and gender mainstreaming in emergencies and working with numerous NGOs including ACT Alliance members, supporting and training their staff on gender issues, child protection, accountability, complaints handling and investigations. She is an experienced investigator herself and has conducted investigations in Asia, South America, Africa and Europe.
Register here for the Webinar on Participatory and Responsive CRM