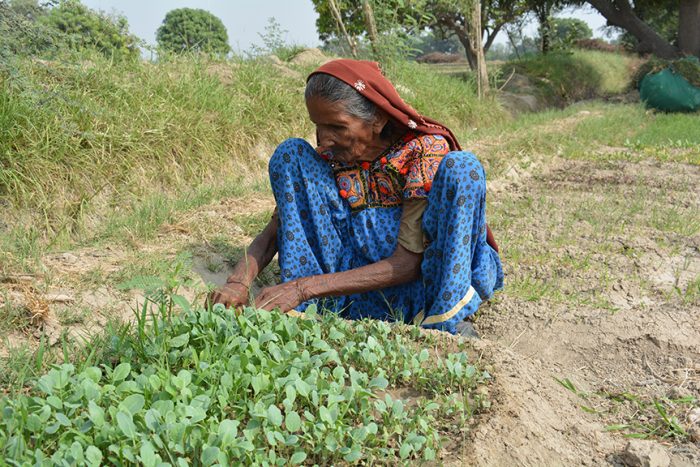
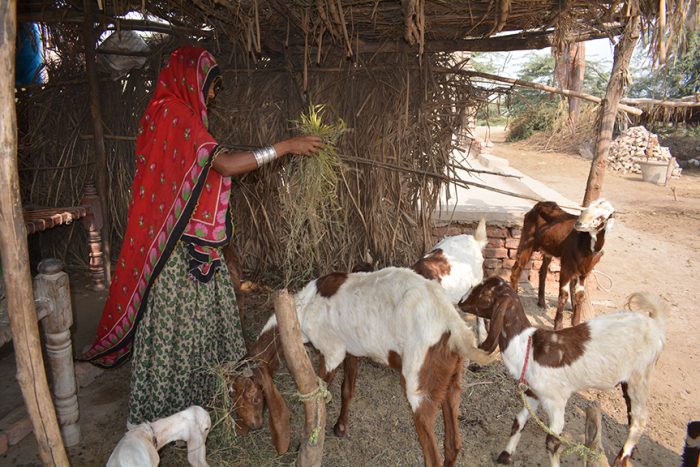
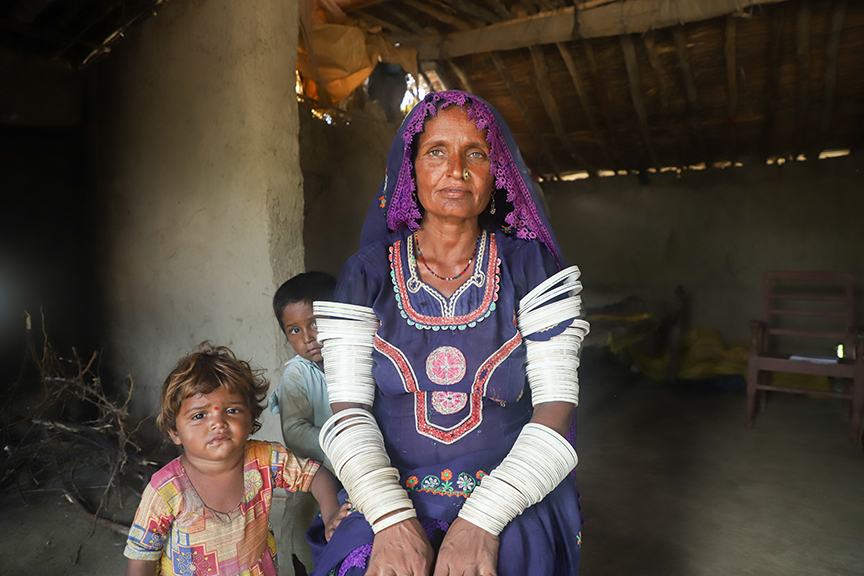
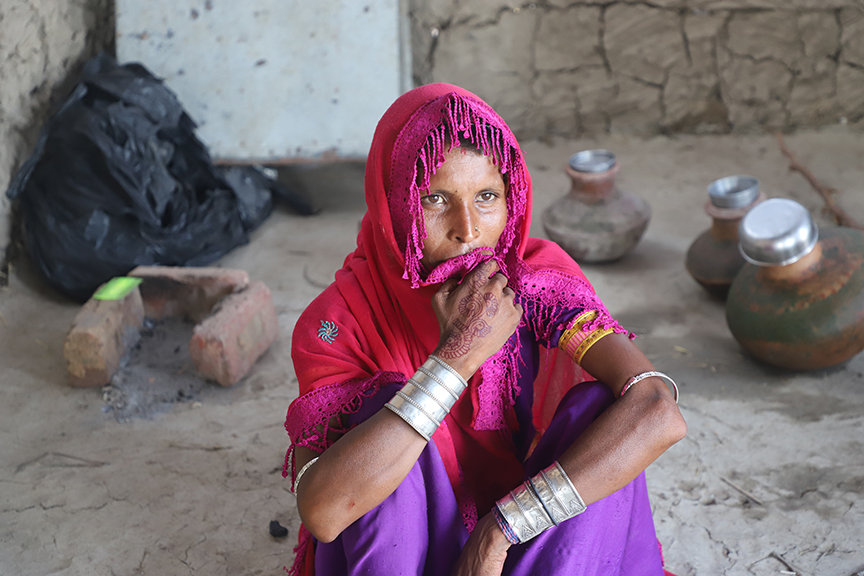
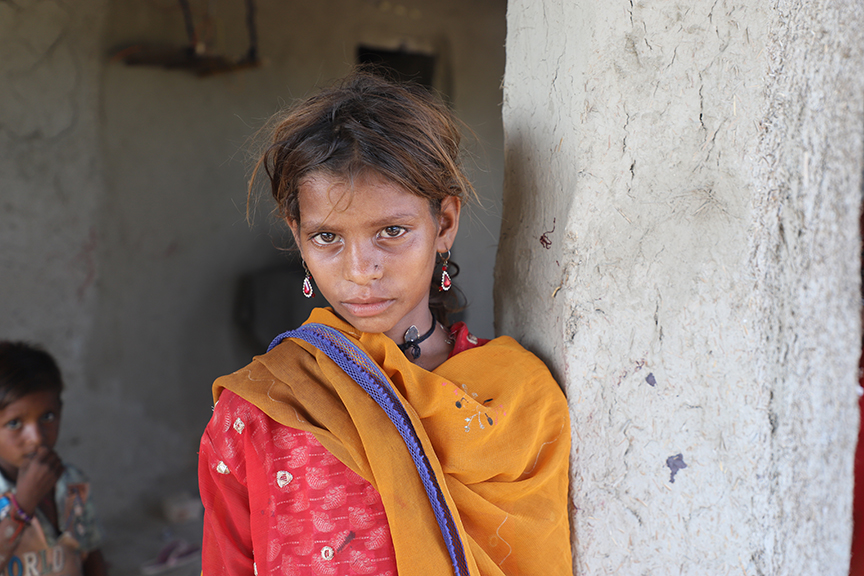
Sabhagi, a 75-year-old widow, has endured a lifetime of hardship. She lives alone in her small mud house in the rural village of Dolat Laghari, in UC Dolatpur of District Mirpurkhas[1]. Since her husband Malhar passed away from a life-threatening illness four years ago, she has faced life alone, drawing on her unwavering strength to persevere. Her only son, now married, lives independently.
For years, Sabhagi worked tirelessly on a small agricultural plot of half-acre, cultivating crops with minimal tools. Farming at her age was physically demanding, and her earnings barely covered basic needs. She remains in debt, though the exact amount is unclear; her landlord maintains the records. Despite the hardships, she continues to toil in the fields daily, her hands worn from decades of labour but her spirit unbroken.
“I had no choice but to keep going,” Sabhagi recalled. “Farming is all I know—it’s what keeps me alive.”
Sabhagi doesn’t own the land she farms; it belongs to a landlord, and she works as a tenant farmer. The arrangement is typically a verbal agreement, where the crop yield or money earned from it is shared on a 50% basis between the farmer and the landowner. Through this, she earns an irregular income of PKR 300–400 (approximately USD 1-1.5) per day. Seasonal vegetables like carrots, onions, cauliflower, radishes, spinach, coriander, turnips, and tomatoes are grown on this land.
The rising costs of seeds, tools, and fertilisers left her struggling for years. However, her fortunes began to shift when CWSA provided essential agricultural inputs—seeds, fertilisers, and tools—and gave a PKR 15,000 (approx.USD 54) cash grant to ease her financial burden. She also received seven different kitchen gardening seeds and training in sustainable agricultural practices, which improved her farming techniques. Now, she expects to earn PKR 500–700 (approx. USD 1.8-2.5) from her kitchen garden. These vegetables will be fresher, healthier, and free from chemicals compared to those sold in the market.
The 2022 floods devastated her village and farmland. She was forced to live in a roadside shelter for six to seven months. Sabhagi faced financial losses, food insecurity, and an uphill battle to rebuild. As an elderly widow and a lone farmer, she continues to face numerous challenges, including physical strain, health concerns, and mental stress exacerbated by isolation and adverse weather conditions.
After taking part in a training on biological pest control methods, disease identification, and the use of organic materials, Sabhagi learned to make neem spray for pest control and compost using organic materials like vegetable waste and farmyard manure. These sustainable practices have improved soil quality and boosted crop yields. “The training was held in our village on October 3, 2024, saving us time and money,” Sabhagi shared. “The seeds and guidance have made farming more productive, and our families now enjoy better, healthier food.”
With newfound knowledge and resources, Sabhagi has noticed improvements in her yield. The kitchen gardening seeds—onion, cauliflower, coriander, radish, spinach, and turnip—have flourished. She uses compost and hand sprays to enhance soil quality and anticipates better crop production in the coming months. This initiative aims to encourage sustainable kitchen gardening practices, improve food security ensuring that households have access to nutritious food throughout the year by equipping farmers with the necessary skills and resources.
Under the Agriculture Support Project supported by Catholic Agency for Overseas Development (CAFOD), CWSA has made a difference in the lives of 899 farmers in Mirpurkhas, providing vital agricultural inputs and cash (PKR 15,000) for land preparation. Farmer selection was conducted through 68 Village Management Committees (VMCs), prioritising widows, people with disabilities, orphans, and families in need. The project spanned 95 villages across two union councils in Mirpurkhas between August 2023 and July 2024. Of the 899 participants, 635 were women, with 100 lead farmers[2] (70% women) receiving targeted support through a two-days training session conducted by a CWSA Trainer to promote community-level capacity building.
In 2023, the lead farmers participated in four comprehensive Training of Trainers (ToT) sessions designed to equip them with specialised skills. These ToTs focused on Crop Selection, Soil Preparation, and Water Conservation Management, Agriculture Management Practices, Harvesting and Post-Harvest Management and Integrated Pest and Disease Management (IPM). Following its completion, the lead farmers returned to their villages to share their knowledge through localised training sessions in their native languages, ensuring accessibility and cultural relevance. This cascading model empowered the broader farming community with practical techniques for improved agricultural practices.
As part of the effort to promote climate-smart agriculture, six fermenters were constructed in collaboration with lead farmers in Mirpurkhas. These fermenters serve as practical examples for farmers, demonstrating effective methods for improving soil health, enhancing organic matter, and increasing soil moisture retention. The fermenters are in the villages of Shahbaz Rangar, Sohbat Laghari, Chodhary Nizamuldin in UC Dolatpur and Yousaf Rajarr, Bhagat Meghraj and Raidhan Colony, UC Taju Khaskheli.
Today, Sabhagi smiles more often, her heart lighter with the knowledge that her hard work is finally paying off. “I’m no longer just surviving; I’m living,” she says. “The support I received has given me new energy and a belief that things can get better, even at my age.”
Her story highlights how timely interventions and compassion can transform lives. What was once a symbol of struggle—her land—now blossoms with hope and promise for a brighter future.
[1] Sindh, Pakistan.
[2] A lead farmer is a trained and experienced community representative who participates in Training of Trainers (TOT). After completing their training, they serve as role models, mentors, and extension agents, sharing knowledge with other farmers in their villages. They promote sustainable agricultural practices, improve crop yields, and work to enhance livelihoods within their communities.
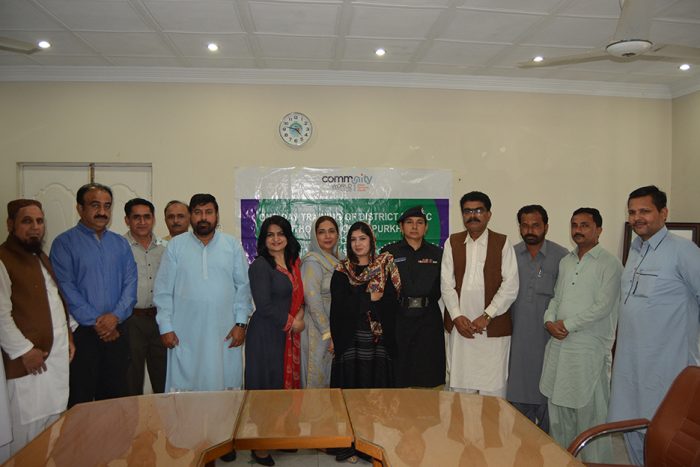


























 “The training was very relevant to our field of work. The training introduced the patriarchy system and how it plays an important role in assigning different roles, keeping in view the gender perspective,” shared Saroop Chand, Assistant Director Social Welfare, Umerkot.
“The training was very relevant to our field of work. The training introduced the patriarchy system and how it plays an important role in assigning different roles, keeping in view the gender perspective,” shared Saroop Chand, Assistant Director Social Welfare, Umerkot. “I mostly decline training proposals I receive. However, the agenda of this training was quite appealing and relevant to my work. Sofia stressed on implementing the existing laws and policies in the country. Through proper implementation, we can omit the gender difference in every field of life and encourage empowerment of both men and women equally for the betterment of our society,” positively expressed Afroza Chohan, Incharge Women Complaint Cell, Mirpurkhas and Umerkot.
“I mostly decline training proposals I receive. However, the agenda of this training was quite appealing and relevant to my work. Sofia stressed on implementing the existing laws and policies in the country. Through proper implementation, we can omit the gender difference in every field of life and encourage empowerment of both men and women equally for the betterment of our society,” positively expressed Afroza Chohan, Incharge Women Complaint Cell, Mirpurkhas and Umerkot. An exercise on clarifying the difference between gender and sex was one of the key topics of one of the sessions. Key institutions, such as family, academia, peer groups, religious institutes and media that play a vital role in establishing societal gender roles were identified as well. “On basis of these roles, some sections of society are given powerful status within societal structures while others are considered subordinate and subjugated. Hence, it is important to emphasize on the difference between gender and sex,” shared Sofia Noreen.
An exercise on clarifying the difference between gender and sex was one of the key topics of one of the sessions. Key institutions, such as family, academia, peer groups, religious institutes and media that play a vital role in establishing societal gender roles were identified as well. “On basis of these roles, some sections of society are given powerful status within societal structures while others are considered subordinate and subjugated. Hence, it is important to emphasize on the difference between gender and sex,” shared Sofia Noreen. “The content of the training was unique and informative. I was unaware of many of the laws and policies related to Gender but this experience built a strong perspective towards women empowerment. The training stressed on how the process of socialization shapes our thoughts and actions and at which level one needs to work on changing the unjust mindsets,” said Junaid Mirza, Assistant Director Social Welfare, Mirpurkhas.
“The content of the training was unique and informative. I was unaware of many of the laws and policies related to Gender but this experience built a strong perspective towards women empowerment. The training stressed on how the process of socialization shapes our thoughts and actions and at which level one needs to work on changing the unjust mindsets,” said Junaid Mirza, Assistant Director Social Welfare, Mirpurkhas.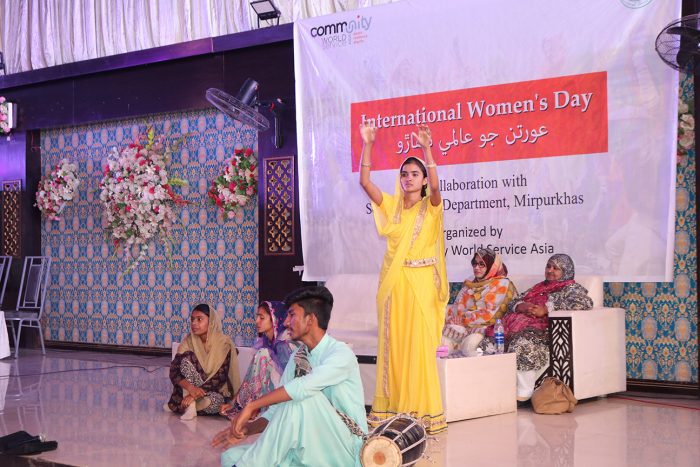



































 MB Khaskheli: The training helped us to understand all the aspects of financial management. This training was designed on building knowledge on basic level. It will be interesting to attend an advanced level training on finance in future. It was an excellent, highly encouraging and full of fun learning experience.”
MB Khaskheli: The training helped us to understand all the aspects of financial management. This training was designed on building knowledge on basic level. It will be interesting to attend an advanced level training on finance in future. It was an excellent, highly encouraging and full of fun learning experience.”

