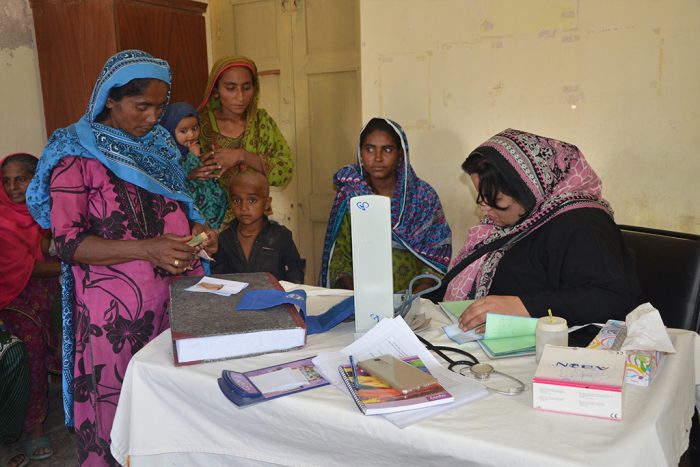
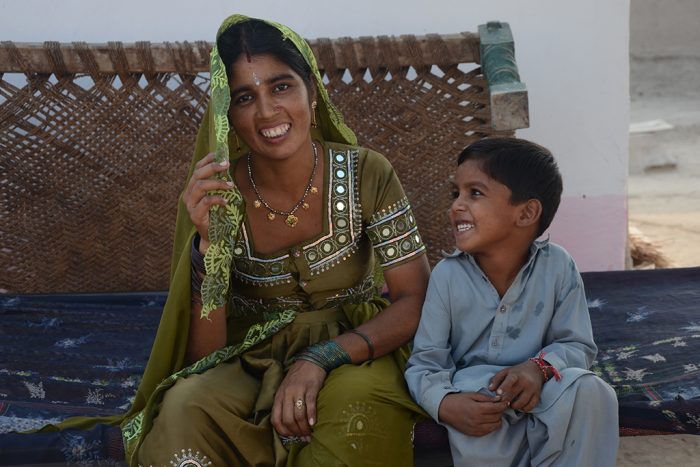
Asiyat Azeem, 36-year-old mother of eight, is a lady health worker (LHW) from Morand Patu village located in Umerkot, district, Sindh Province. She has four daughters and four sons.
Asiyat added that her two elder sons are not employed due to lack of education.My husband is an old man and does not work. I am the sole bread earner in my house. As a LHW with the health department, I earn a salary of PKR 21,000 monthly. My income is mostly consumed in household expenses.
With my little savings I could not afford their education, I therefore set up a small grocery shop for my eldest son. He earns around PKR 300 – 500, varying on the daily sales. There are days when they there are no sales even. My second son assists me in my activities as a health worker.
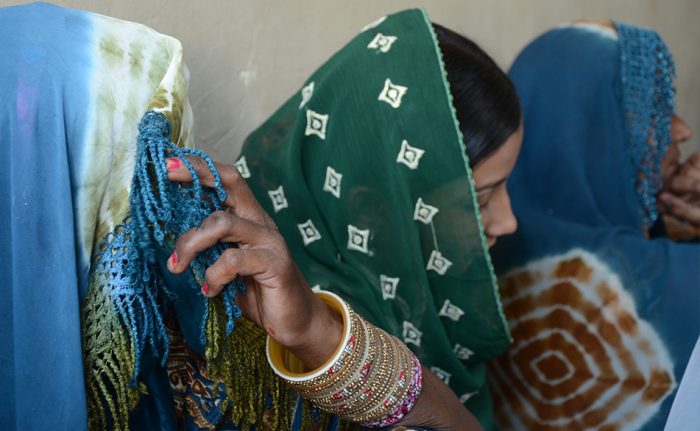
Women in Morad Patu lived a conservative life and were not allowed to travel freely on their own. They rarely stepped out of their homes and if they ever did, it wouldn’t be without the men in their families accompanying. Most of their days were spent taking care of their children and families and completing daily home chores. Some of the women stitched clothes for their families and children in their spare time; however, their skills were not utilized to earn money.
Since Asiyat has been bearing all financial responsibilities on her own, she was unable to send all her children to school. However, Asiyat made sure to send her three younger children to a local school in the district to avail education. Of the three, two of her sons attend classes one and four and the daughter is in class five. Asiyat’s eldest daughter is married and has four children of her own, while her second daughter is working as an artisan in the vocational center set up by Community World Service Asia and Ycare.My son, who works as a health worker with me, has been very supportive. He travels to far cities to purchase medicines and vaccines. Together, we then give vaccinations and conduct other health inducing activities together in Morand Patu and nearby villages.
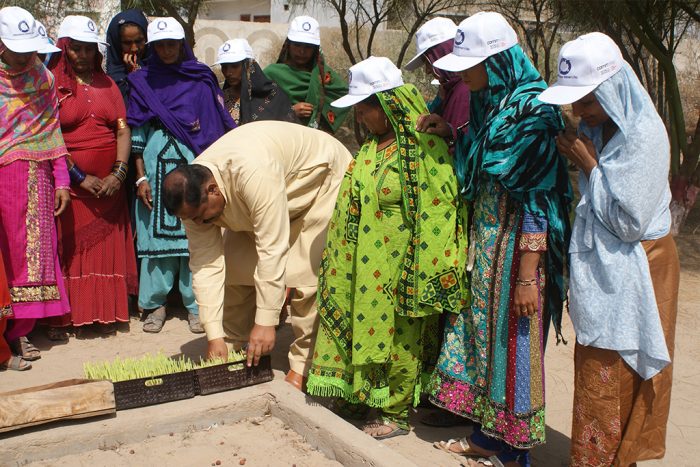
Community World Service Asia’s project team came to the Kharoro Charan village in 2017 to identify new villages for inclusion in their Livelihoods’ project. There, at the village health center, they met Rasheeda, a prominent gender activist from the village, and a few lady health workers (LHWs). Krishni, a LHW, was among the participants at the meeting. After their meeting, Krishni met Asiyat and told her about the initiative and shared contact details of the team with her. In response, Asiyat was quick to call and invite the livelihoods team to her village as she had a strong desire to bring development opportunities to the village and to improve her communities’ standards of living.
Naheed, a Community Mobilizer working with Community World Service Asia, shared,
When we first came to Murad Patu, all the girls hid in their homes and stared at us from a distance. No girl or woman was ready to sit for the skill assessment and join the center for skills development. The men in the village thought that we, the women representing the organization, will work against their cultural norms and will encourage women to disobey their families and men and leave their homes to build a future for themselves.
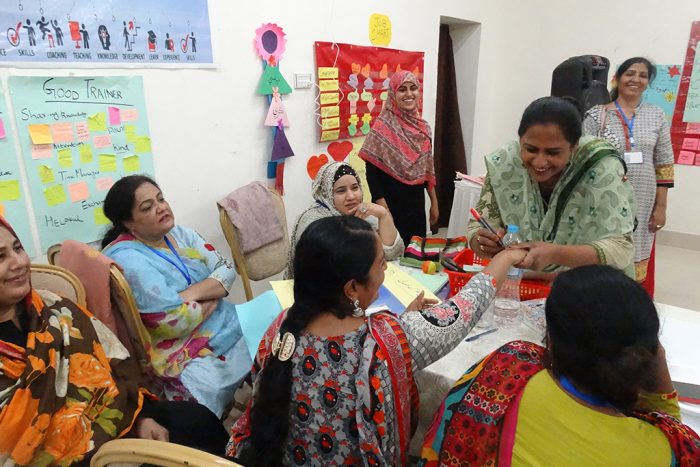
To bridge these social barriers between the project team and the community, Asiyat gathered a few elder community members (men and women) of the village and conducted a joint meeting to brief them about the project, its interventions and the establishment of the vocational center. In the beginning, Asiyat dedicated a room in her own to be used as the vocational center as part of the project. As more and more artisans, started registering, it was getting difficult to accommodate all of them in that room. Moreover, the natural light (being the only source of light in the room during long hours of electric load shedding) was insufficient to continue the lessons and intricate handwork. Asiyat discussed these issues with Arbab, the President of the village Steering Committee, who, vacated a room in his son’s house in the village to use as the vocational center. This room was much bigger in size and had more windows which allowed sufficient natural light to enter the room. The forty-five artisans selected at the centre were divided in groups of three; each group worked for two hours daily at the centre.
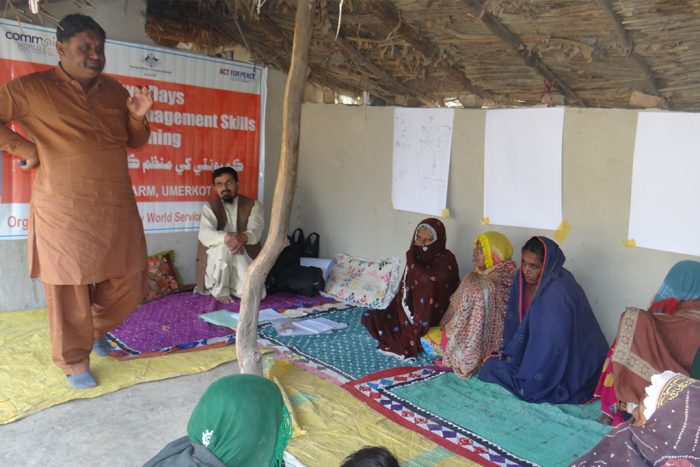
As a gender activist, I was given six households to work with and raise awareness on gender related issues. I held meetings with all households individually and observed their issues closely. After identifying their problems, I worked with each household accordingly. In the initial meeting I briefed the families about gender equality, the negative impacts of early and childhood marriage and gender discrimination. Through a booklet consisting of pictorial flip charts, delivering clear messages, it was easy to explain to the families the importance of gender equality in a society.
The views and opinions of the women in Murad Patu were generally overlooked and they had no input or say in decision-making processes. After Asiyat starting meeting these families and initiated candid discussions on prevalent issues with them, the women started to open up and participate in decision-making, especially regarding decisions relating to their children and their marriages.
shared Khatoon, a woman residing in Murad Patu.When a proposal comes for a girl, both the parents take a mutual decision whether to accept or refuse the proposal. We speak up when we disagree with any decision taken up by the men in the family. Before, it was impossible to say anything as the decision made by the elders was considered as the last verdict,
Most girls in the village rarely attended school and many of them just played in the village instead of attending school. Asiyat narrated,
I encouraged mothers to send their children, especially girls, to schools as this education will be beneficial for their future. I explained to them, if a girl is educated, she will be able to support her family financially in bad times and make important decisions for them. Women here never thought of their future before, therefore they do not encourage their daughters to be prepared for bad times either.
Zainab, a resident of Morad Patu, recalled,
My daughter did not go to school. My family was amongst the six households assigned to Asiyat to work with. She came to our house and told us why education is important, especially for girls. I did not think for the better future of my daughter. But today, I am happy to share with you that my daughter goes to school regularly and I wish to see her grow intellectually.
Fehmida and Gulzaab, daughters of Merab, another mother from Morad Patu, also started attending school after Asiyat encouraged the family to do so and enlightened them about the need and significance of education for a happy and progressive life.
Early and child-hood marriages were a common practice in the village. Girls of Morad Patu would customarily be married off by the age of 15years. Asiyat shared,
Due to the rigid mind-set and cultural norms, the people here never measured the disadvantages of marrying young girls. Shahnaz, 13 years old, and Farzana, 14 years old, were to be married in December 2017. Knowing the problems young girls face due to early marriage, I met with their families individually to try to talk them out of marrying their young daughters at such a young age. The families were told about the burden we put on young lives which affects their health badly. Moreover, I explained the complications girls face during pregnancy at young ages, badly affecting the health of the mother and child. I gave them an example of a minor girl in our village who was married and consequently experienced three miscarriages due to which her health seriously deteriorated. Upon knowing the severe risks girls face in early marriages, the families of both the girls postponed their marriage for five years. Today, both the girls are happily working in the vocational center as artisans and earning through the local orders they receive.
Among the twelve hundred villagers living in Murad Patu, Asiyat was the only woman who worked independently, stepping out of her house to earn a living for her family.
After continuous meetings in relation to gender equality, we have 45 artisans working actively in the vocational center and contributing financially in their households. Three of the artisans travelled to Umerkot City and Chor (a city near Umerkot) to shop for their families and children. This was a great achievement.
I believe that women should be able to come out and take decisions for themselves. Mostly women do not share their opinions or wishes and only dream of being given importance. I encourage women to believe in themselves and take action to achieve their dreams. My son, who assisted me in my health activities, is also a gender activist under the livelihoods project. I am glad to see that my son is also working for women empowerment.