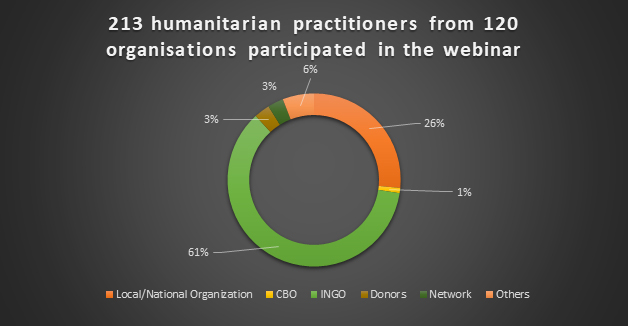
New Approaches to Monitor Remote Programming during COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted global humanitarian and development programming. It has severely affected aid organisations’ capacity to execute field activities and track project implementation, challenges and progress. Inaccessibility to project locations and restricted direct physical contact with communities represent significant challenges to conventional M&E operations.
Understanding community’s situation – their needs, values and problems – is essential for aid organisations to respond effectively. COVID-19 and the ‘lockdown’ restrictions imposed in response, have led to some program operations being suspended or discontinued and in this case it is critical to consider the impact of these closures on the communities. Other programs that have continued amid the pandemic, adopting new methods and modalities for implementation and it is important to understand how new way of programming are meeting communities’ needs.
The pandemic has pushed us all to reassess and prioritise the types of evidence and data we need to inform programmes and adapt Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) strategies to the new environment. To share experiences and best practices and facilitate a productive discussion on monitoring and evaluation during the pandemic, Community World Service Asia and INTRAC jointly hosted a webinar on remote monitoring in the context of COVID-19 on August 11.
Dan James, Principal Consultant and Thematic Lead at INTRAC moderated the session and was joined by speakers Dylan Diggs, Monitoring and Evaluation Specialist, The State Department’s Democracy (DRL), M. Said Alhudzari Bin Ibrahim, General Manager – Programme Operations, MERCY Malaysia, Jonah S. Nobleza, Program Manager, Market Development and Financial Innovations for Agriculture at ICCO Regional Office Southeast Asia & Pacific, Michael Kendagor, Coordinator Emergency Response and DRR at Church World Service and Aung Phyo Thant, MEAL Coordinator with FinChurch Aid.
For those of us working in the humanitarian and development sector, the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as the measures taken by our respective governments to combat the virus, have created unique challenges for programs and their functioning. The session focused particularly on how the pandemic has affected monitoring and how to effectively monitor program when access to communities and people who we are working with is restricted.
What has and has not changed with COVID-19?
There are three broad areas where challenges and changes can take place as a result of COVID-19. These include:
- Organisations’ ability to access communities restricted
- Organisations ability to carry out programmes in usual way
- Community needs and situation
“The lockdown measure, social distancing, the variety of interventions governments and local authorities have to make actually means that our access to communities for monitoring purposes can be limited or cut off completely in some cases, or curtailed in different ways. These restrictions, lead to changes in program delivery,” shared Dan, “The virus has also changed the needs and situations at community level. Thus, there is real need to have up-to-date information on how the situation is changing and how the communities’ needs are shifting.”

Have monitoring needs changed as a result of COVID-19?
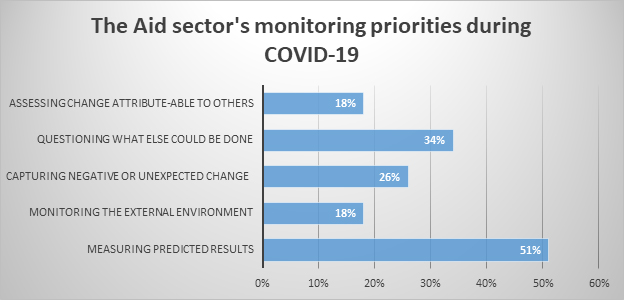
We asked participants in a quick poll to share their top monitoring priority during the pandemic. While measuring predicted results is still a top priority (often for accountability purposes), understanding negative/unanticipated impacts on communities and questioning what else can be done to support communities are more important during the pandemic than during normal times.
There are however, some things that have not changed: the need for basic information about project and programme delivery, donor requirements for accountability data about programmes and organisational capacity for programming and M&E.
Dan reminded participants that we must “work with what we have” in terms of capacities, resources, relationships and structures as the pandemic has not given the global aid community the time to prepare and develop ideal strategies to combat the situation.
Best Practices of Remote Monitoring in the COVID-19 Context
Working through volunteers using a HUB based approach – Mercy Malaysia
“The traditional approach where our M&E staff travelled to target areas to monitor was no longer an option due to the inter-state travelling ban. Mercy Malaysia established a complete separate COVID-19 Operations Hub whose functions included planning, verification, procurement, data consolidation and reporting,” shared M. Said.
The model Mercy Malaysia adopted for the Remote Monitoring of their project consist of the following steps.
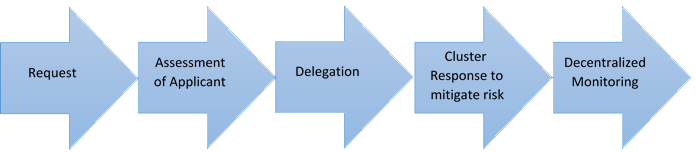
Most of the operations of the Hub were based in Kuala Lumpur, but Mercy Malaysia handled the responses of all fourteen states of Malaysia.
Using Mobile-based Technology for Engaging Communities – ICCO
“As soon as COVID-19 induced restrictions were enforced, consortium members in Myanmar developed a business continuity plan to mitigate the risks of further delays in implementation. We decided to customize a remote, mobile – based, methodology to conduct interviews and collect data from our target groups and beneficiaries,” shared Jonah.
Digital Cash Transfer to Prevent the spread of COVID-19 – Church World Service (Africa)
As another example, Church World Service (Africa) shifted their approach to response and monitoring towards digital and virtual platforms when Kenya was affected by multiple natural disasters, conflict and eventually COVID-19. Digital cash transfer was utilized using the M-Pesa platform in partnership with the bank and mobile service provider (Safaricom).
Michael shared that CWS now has a database of program participants in the various locations which are acquired through identification and profiling. This is done through kobo tool kit that enables real time processing of data. Once cash transfer has been undertaken, the monitoring and evaluation team of the organisation conducts a post distribution assessment to determine the efficiency and effectiveness of the response as well as its impact in the lives and livelihoods of the target beneficiaries.
Keeping the Hope Alive – Fin Church Aid
“As a result of COVID-19, children were forced to stay at home as schools were shut down amid coronavirus. In Fin Church Aid, we wanted to learn the psychological well-being of children, staying at home. To assess this situation, we conducted assessments using the online data tools, which allowed us to reach to respondents without in-person contact during this pandemic. We conducted assessments via Kobo Toolbox[1] and mobile phones,” shared Aung.
US State Departments Democracy Rights and Labor Division
Dylan Diggs, from US State Departments Democracy Rights and Labor division shared thoughts about working with donors on adapting M&E. DRL provides M&E assistance to grantees throughout the life cycle of the program.
“Even before COVID-19, we have had a flexible approach to M&E. We believe that our implementers know best. This doesn’t mean that we expect everyone to be an M&E expert. But, we do believe that M&E can be done by qualified internal evaluators and program staff that are interested in using M&E principles for logical program design and evaluation,” said Dylan.
Dylan highlighted four important considerations to adapting M&E during the current pandemic.
![]() Assess Plans & Approaches: Encourage organizations to rethink M&E plans and review anticipated results
Assess Plans & Approaches: Encourage organizations to rethink M&E plans and review anticipated results
![]() Adjust your M&E approaches and methods: Update your M&E to the new environment while reviewing indicators and consulting beneficiaries on contingency plans
Adjust your M&E approaches and methods: Update your M&E to the new environment while reviewing indicators and consulting beneficiaries on contingency plans
![]() Adapt Your Operations: Communications Methods are changing by adopting digital methods, phone interviews and monitoring with photographic and video evidence
Adapt Your Operations: Communications Methods are changing by adopting digital methods, phone interviews and monitoring with photographic and video evidence
![]() Do No Harm: This comes in play in digital protection and in-person approaches including use of Personal Protective Equipment and maintaining social distancing
Do No Harm: This comes in play in digital protection and in-person approaches including use of Personal Protective Equipment and maintaining social distancing
Participants’ Thoughts
Towards the end of the webinar, participants raised questions regarding verification being applied by different entities. M. Said responded,
“Yes we do. Besides verification through other than the requesting party, we do have a local government agency, in Malaysia’s case the Welfare Department, who has data on vulnerable communities as well. However, they are not the only source of information for us.”
Another participant queried on how to monitor the progress or activities in remote settings where there is no access to any kind of communication modes. M. Said answered,
“Simplify the process and empower the local community to participate in monitoring. It is essential to know that programmes are more effective with community involvement.”
Participants highlighted data as the most frequently term used during sessions. They questioned if there is a healthy tension between data and people, in terms of their current contextual realities. Dan answered by saying,
“Definitely – our view is that monitoring needs to prioritise people. There is a need to review – perhaps from scratch – the kinds of data we are looking for to ensure monitoring activities are both low risk and have benefits for people.”
A total of 73% of the webinar participants found learning practical methods for remote monitoring as the most interesting discussion point. However, they raised questions on “How organisations can ensure fair and unbiased remote assessments with only identified community members interviewed rather than a random selection? To this, the facilitators responded,
“We collaborated with communities and local organizations actively to ensure that assessment is not biased. In addition, we involved religious leaders who tend to be influential people within communities but that did not restrict us from communicating with the communities directly. It is essential to involve local NGOs as they have direct interaction with the communities and therefore they are able to assist effectively and identify affected populations who are in dire need of assistance.”
[1] KoBoToolbox is a free toolkit for collecting and managing data in challenging environments and is the most widely-used tool in humanitarian emergencies.








