Mainstreaming Quality and Accountability for effective Aid Response
“Quality & Accountability Mainstreaming is a process, a journey of bringing specialized areas into the main flow of our humanitarian work. In this case, it is Accountability. The question is how is it done? What are the steps taken? What are the processes that are put in place?”
Uma Narayanan, HR and OD Consultant, raised these questions while moderating the webinar on ‘Mainstreaming Quality & Accountability’ on November 20th. As a kick-start to the 2020 Regional NGO Partnership Events, the webinar was hosted and organised collaboratively by Community World Service Asia (CWSA), Asian Disaster Reduction and Response Network (ADRRN), International Council of Voluntary Agencies (ICVA) and United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (UNOCHA).
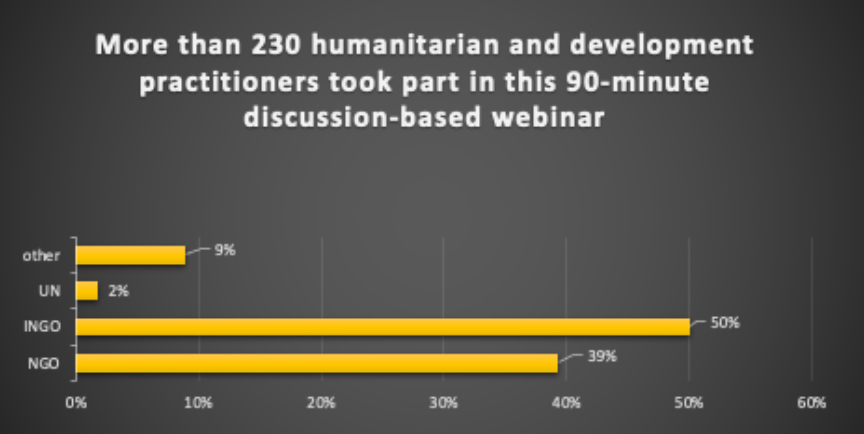
The 2020 Regional NGO Partnership Events are an online journey of three months, starting with a consultative meeting on ‘the future of humanitarian response in Asia and the Pacific’, followed by various consultations and webinars, and a research that will produce a policy paper on the sector’s future in the region.
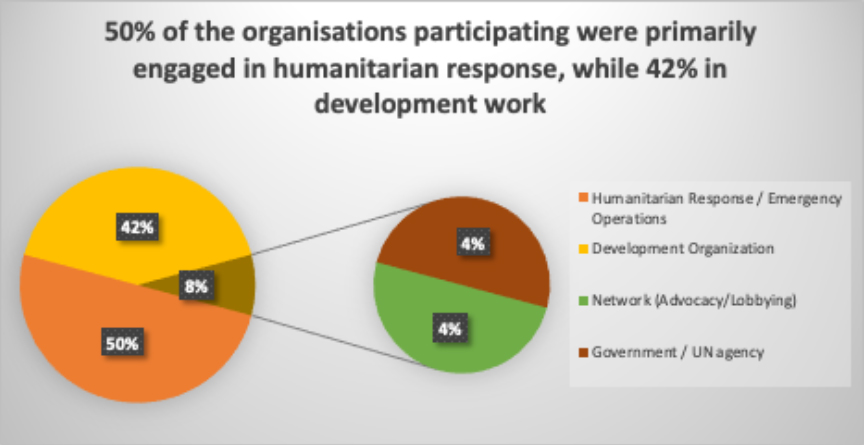
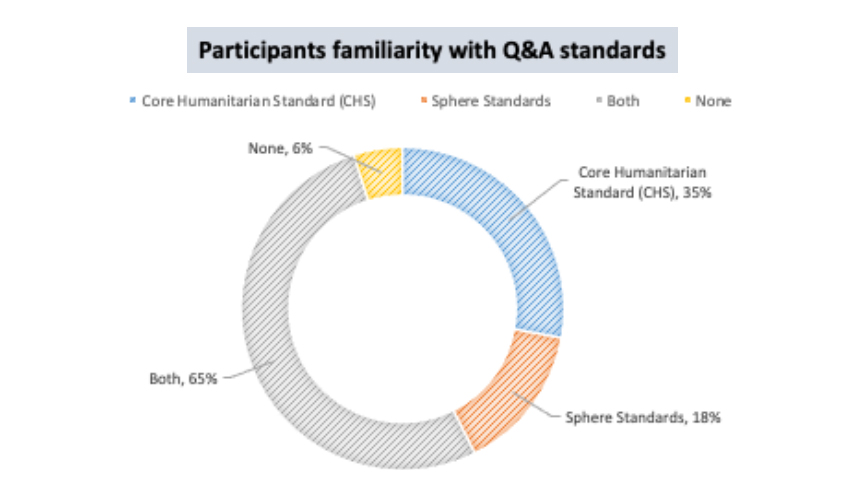
The participants were asked about their familiarity and experience working on Q&A standards. 65% of the participants were familiar with both, the Core Humanitarian Standard (CHS) and Sphere Standards, while 6% were not yet familiar with Q&A standards.
What is Q&A Mainstreaming?
“It is a process to integrate Q&A into existing frameworks and practice and make institutional changes. This is done by linking the organisation’s mandate and thematic areas and aligning organisation’s vision and commitment with Q&A,” said Uma during the session. “It is about ensuring accountability is part of your organisation’s DNA,” said Uma.
The webinar explored different entry points of Q&A mainstreaming. Some organisations do it through CHS certification process; some others start, at project level, such as setting up Complaint Response Mechanism (CRM). Numerous organisations implement accountability mechanisms as part of the donor’s requirements in terms of ensuring certain policies, processes and mainstreaming accountability in M&E[1].
What are the barriers to Q&A mainstreaming?
Participants discussed the various obstacles that many organisations face while mainstreaming Q&A in their framework and practices. Some challenges included diverse culture of communities and organisations, lack of technical expertise, lack of management ‘buy-in’, various mismatched expectations, accountability is linked to project durations and limited resources and time, lengthy certification process.
Bonaventure Sokpoh, from CHS Alliance, added here, “We have updated the CHS self-assessment manual in a way that is survey-based and much easier for organisations to take and use. Every individual, i.e. your key stakeholders, can take some time out to answer key questions. The result of the survey will help to learn meaningful reflections of the organisation in terms of Q&A, making it less time-consuming for all functions.”
The Responsibility Matrix: Key Players in Mainstreaming Q&A
Within the organisation, there are key players who have an essential role in mainstreaming Q&A in the organisational framework and thematic areas. Here is a quick introduction to these players:

- Allocate Resources
- Align Policies
- Model Q&A Behavior
- Create Q&A Culture

- Implement Q&A in Programme
- Makes changes to programme based on feedback
- Share examples of best practice

- Listens to stakeholder & purchase quality service & products
- Makes changes based on feedback

- Select staff that are Q&A compliant
- Build staff capacity on Q&A
- Revise HR policies, procedures that is competency based

- Budget allocation for Q&A
- Ensures financial donor commitments are met
- Ensure Anti-fraud measures and auditing
- M&E processes & tools integrates Q&A
- Help set up Q&A mechanism
- Analyze complains
Key Reflections
- Q&A is a Shared Responsibility
Rizwan Iqbal, Quality and Accountability Coordinator, ACT Alliance, shared a key aspect of Q&A, that is shared responsibility.
“In my experience, I have witnessed that accountability is not one person’s responsibility. To achieve shared responsibility, while working in Community World Service Asia before joining ACT Alliance, we built capacities of internal and external stakeholders. The team members, who were directly involved and supporting the Q&A programme, were trained through in-house training programmes to enhance knowledge of Q&A and how to link Q&A to their role and job responsibilities.
Resource allocation for Q&A as a challenge in many organisation but there are some ways to overcome them. Organisations lacking in resources, are encouraged to show more commitment towards accountability by taking small steps. This will strengthen your standing in the development sector and more support can come your way.”
Learning Resources on Q&A:
- Client Responsiveness Measurement Framework: https://www.rescue.org/sites/default/files/document/3605/irc-clientresponsivenessmeasurementframework-digital.pdf
- A Guide for Client Responsive Staff Management: https://www.rescue.org/sites/default/files/document/3603/irc-hrguideresponsivenessframework-digital.pdf
- The New CHS Self-Assessment manual: https://www.chsalliance.org/get-support/resource/chs-self-assessment-manual/
- online resources to build capacity of staff: disasterready.org, https://fabo.org, www.kayaconnect.org
- Q&A E-Courses short-listed by CWSA from KayaConnect: https://kayaconnect.org/local/curatedcontent/context.php?id=44
[1] Monitoring & Evaluation







